Health Pages
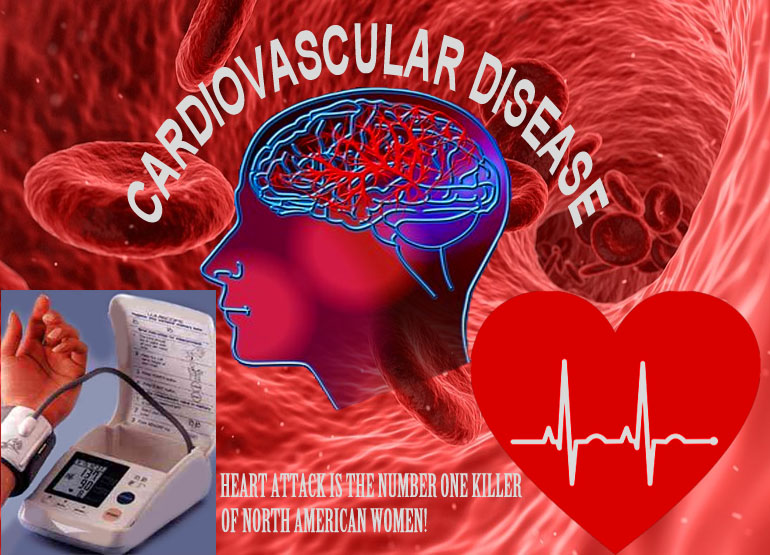
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the collective term for various forms of diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Heart attacks and strokes are the most common life-treatening manifestations of cardiovascular disease.
Most people typically think of cardiovascular disease as primarily affecting older adults or men, but heart attack is the number one killer of North American women. Also women with diabetes have a greater risk of having CVD events like heart attack and stroke than men with diabetes.
Much of the incidence of cardiovascular disease is due to our modern way of life. Too many people live sedentary life, eat an unhealthy diet, smoke, manage stress ineffectively, have uncontrolled high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels, and don't know the signs of cardiovascular disease. Find out more about CVD disease risk factors...
According to World Health Organization's Fact Sheet , an estimated 17.7 million people died from CVDs in 2015, representing 31% of all global deaths. Of these deaths, an estimated 7.4 million were due to coronary heart disease and 6.7 million were due to stroke.
MAIN FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
The main forms of cardiovascular disease are:
 Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis
 Heart Disease
Heart Disease
 Heart Attack
Heart Attack
 Stroke
Stroke
 Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
 Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congenital Heart Disease
Congenital Heart Disease
 Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic Heart Disease
 Heart Valve Problems
Heart Valve Problems
Note: Many forms of cardiovascular disease are interrelated and have elements in common. Your chances of developing cardiovascular disease depend on a variety of factors, many of which are under your control. The best time to identify your risk factors and change your behavior to lower your risk is when you are young.
Below are links and information you need to know to make smart choices in your life and help your to make changes and take charge of our health.
Good to Know Information:
 CVD Disease Risk Factors
CVD Disease Risk Factors
 Heart Disease
Heart Disease
 Cholesterol and You
Cholesterol and You
 Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10
 Antioxidants
Antioxidants
 How Dead is Your Diet?
How Dead is Your Diet?
 The Power Of Relaxation
The Power Of Relaxation
 Meditation For Health Purposes
Meditation For Health Purposes
 Teasting Treatments
Teasting Treatments
 First Aid
First Aid